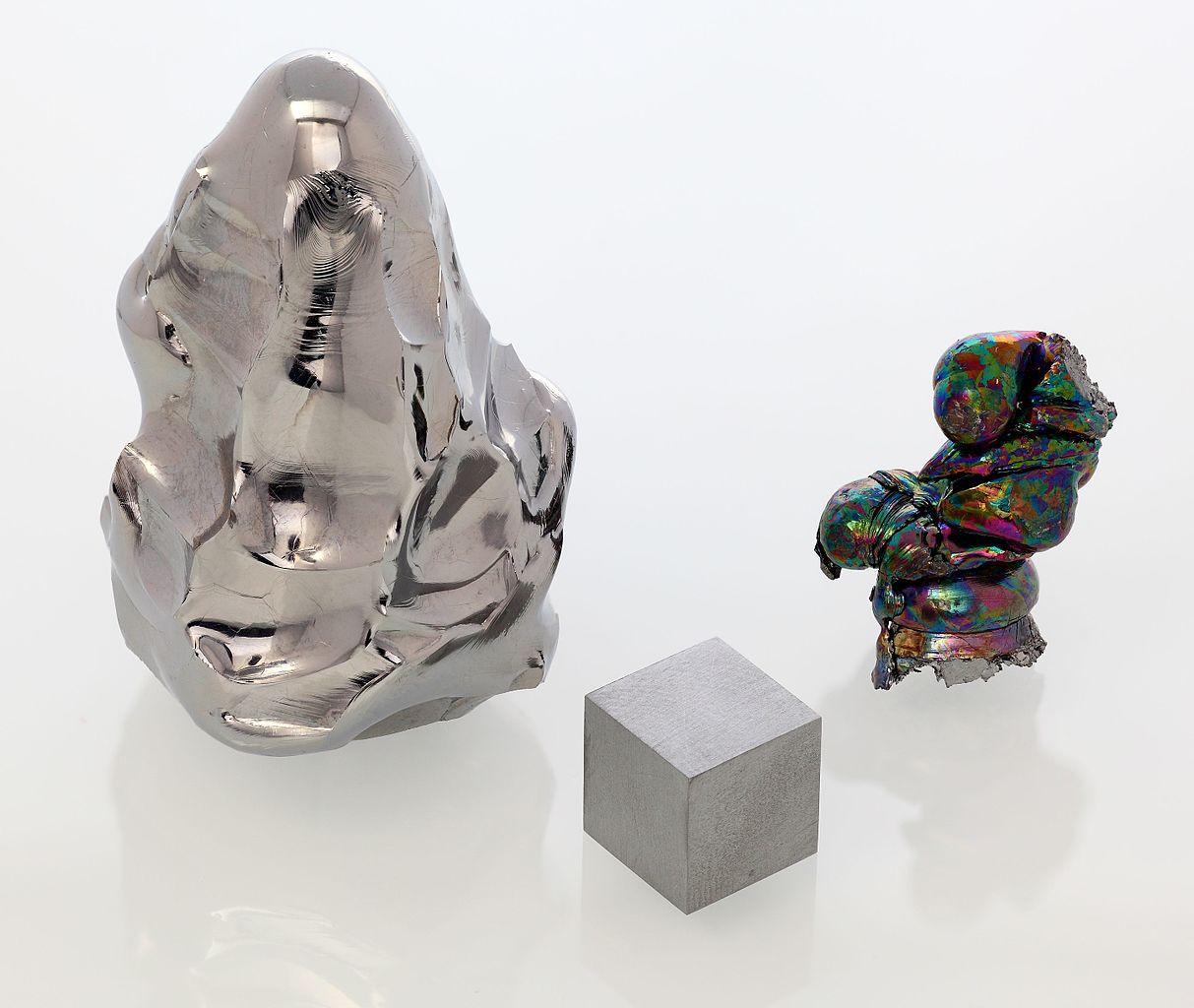
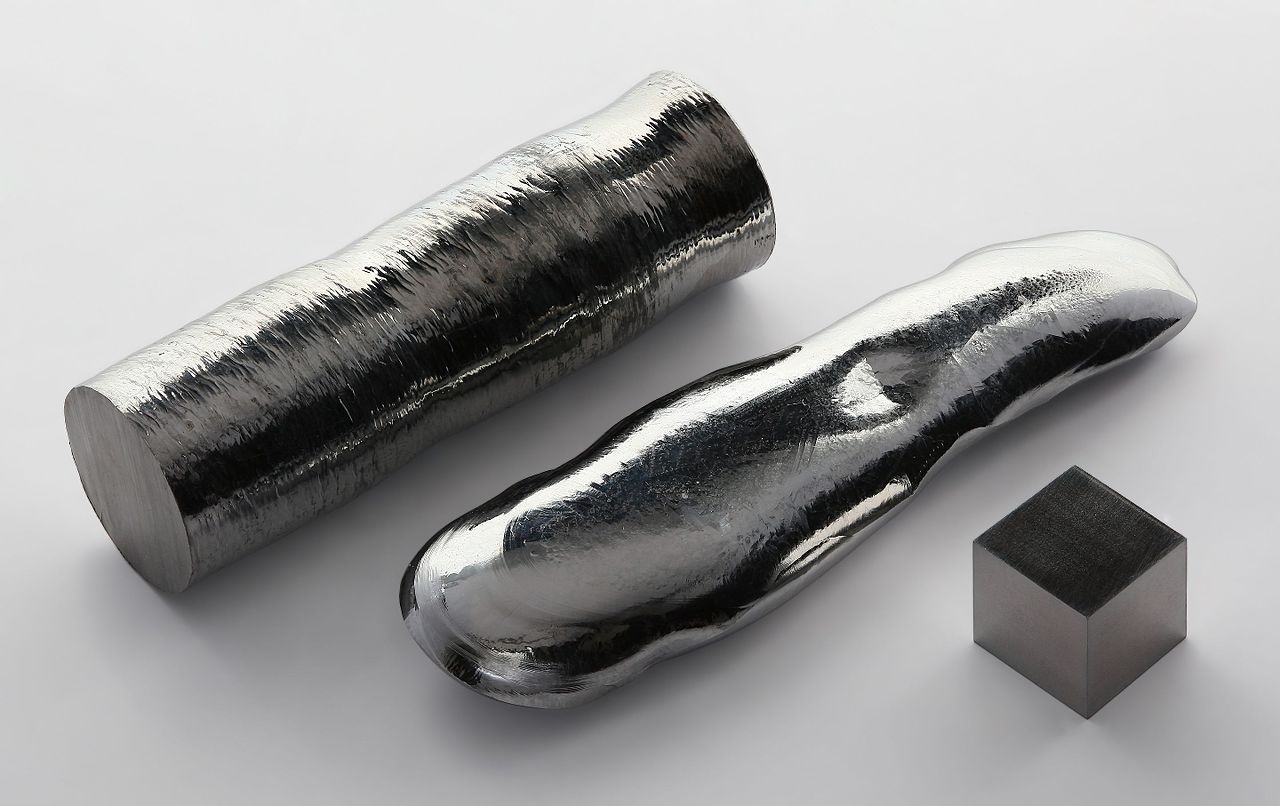
Tantalum is a shiny silvery metal that is heavy, dense, malleable and ductile when pure.
Tantalum is extremely resistant to corrosion due to the formation of an oxide film.
It is also resistant to attack by acids (except hydrofluoric acid).
It reacts with molten bases and various non-metals at high temperatures.
Tantalum can be used as a substitute for platinum in laboratory equipment requiring high corrosion resistance.
This metal is also used in the chemical industry for similar reasons.
Fluids in the human body do not react with metal and therefore it is used for surgical implants without risk of rejection.
Pure metal is used in the electronics industry for the production of various types of electronic equipment (rectifiers, capacitors, lamp filaments, etc.).
Tantalum is also used in vacuum systems due to its high residual gas absorption rate.
It is also used as an alloying element with, for example, nickel and
molybdenum, to produce alloys that have high resistance to corrosion, high strength and good ductility.
Le
Niobium is almost always found associated with tantalum.
Niobium has many uses, some of which are shared with other refractory metals.
It can be annealed to obtain better elastic strength. It is the least dense of the refractory metals. It can be used in electrolytic capacitors and in superconducting alloys.
It is also found in aircraft gas turbines, electronic tubes and nuclear reactors.